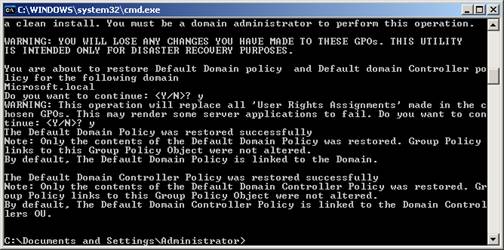
Modify the usbmount.bat script
1. Using a text editor such as Notepad, edit the usbmount.bat script according to your requirements. The following attributes must be set:
2. Set the username, password and address (IP or hostname) of your XenServer host:
SET XE_USERNAME=root
SET XE_PASSWORD=CHANGEME
SET XE_SERVER=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
3. Determine the universally unique identifier (UUID) of the Storage Repository that corresponds with the Removable Storage. You can determine this by running the following command from within your XenServer host console:
xe sr-list name-label=Removable\ Storage
4. Once you have the UUID of the Removable Storage, make the change to the script:
REM Removable Storage Repository UUID
SET REMOVABLE_SR_UUID=CHANGEME
5. Determine the UUID of the virtual machine (VM) you wish to attach the storage to. To do this, run:
xe vm-list
6. With the UUID of the VM, make the change to the script:
REM UUID of the VM you wish to attach the USB storage to
SET VM_UUID=CHANGEME
7. Set the device order. It is important to ensure that there is no overlap and this is done by looking at the number of devices attached to the VM. For example, if only one storage device is currently being used (example: virtual hard disk), the next device name to use will be hdb.
REM Device name/order on the VM (example: hdb, hdc, hdd…)
SET DEVICE_NAME=hdb
8. Run or Schedule the Batch Program
9. Once you have made the changes to the batch program, test it by running it from a Command Prompt window. Note that the utility requires a parameter, otherwise it exits.
10. To attach the USB storage device to the VM, run:
usbmount.bat ATTACH
11. To detach the USB storage device from the VM, run:
usbmount.bat DETACH
Listing of USBMOUNT.BAT
@ECHO OFF
setlocal
REM Attach a USB flash device to a specified VM on XenServer 4.x
REM ————- EDIT THE OPTIONS BELOW TO SUIT YOUR ENVIRONMENT ————-
REM XenServer Credentials
SET XE_USERNAME=root
SET XE_PASSWORD=CHANGEME
SET XE_SERVER=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
REM Removable Storage Repository UUID
SET REMOVABLE_SR_UUID=CHANGEME
REM UUID of the VM you wish to attach the USB storage to
SET VM_UUID=CHANGEME
REM Device name/order on the VM (e.g. hdb, hdc, hdd…)
set DEVICE_NAME=hdb
REM —————————————————————————
REM XenCenter Path
SET XE_CENTER_PATH=C:\program files\citrix\XenCenter\
REM XE Binary and Baseline Parameters
SET XE_EXEC=”%XE_CENTER_PATH%\xe.exe” -s %XE_SERVER% -u %XE_USERNAME% -pw %XE_PASSWORD%
REM Temporary working file
SET TEMP_FILE=%TEMP%/xs-usbmount.tmp
REM ———— DO NOT EDIT BEYOND THIS LINE —————-
IF “%1″==”ATTACH” GOTO ATTACH_STORAGE
IF “%1″==”DETACH” GOTO DETACH_STORAGE
REM No parameters
echo Usage USBMOUNT.BAT ^<ATTACH ^| DETACH^>
GOTO END
:DETACH_STORAGE
%XE_EXEC% vdi-list sr-uuid=%REMOVABLE_SR_UUID% params=vbd-uuids –minimal > %TEMP_FILE%
SET /P VBD_UUIDS= < %TEMP_FILE%
IF “%VBD_UUIDS%”==”” GOTO NOT_BOUND
%XE_EXEC% vbd-unplug uuid=%VBD_UUIDS%
%XE_EXEC% vbd-destroy uuid=%VBD_UUIDS%
echo.Storage Detached
GOTO END
:ATTACH_STORAGE
REM See if the storage is already bound to a VBD
%XE_EXEC% vdi-list sr-uuid=%REMOVABLE_SR_UUID% params=vbd-uuids –minimal > %TEMP_FILE%
SET /P VBD_UUIDS= < %TEMP_FILE%
IF NOT “%VBD_UUIDS%”==”” GOTO ALREADY_BOUND
%XE_EXEC% vdi-list sr-uuid=%REMOVABLE_SR_UUID% params=uuid –minimal > %TEMP_FILE%
SET /P VDI_UUID= < %TEMP_FILE%
%XE_EXEC% vbd-create vm-uuid=%VM_UUID% device=%DEVICE_NAME% vdi-uuid=%VDI_UUID% –minimal > %TEMP_FILE%
SET /P VBD_UUID= < %TEMP_FILE%
%XE_EXEC% vbd-plug uuid=%VBD_UUID%
echo.VBD UUID attached as: %VBD_UUID%
GOTO END
:ALREADY_BOUND
echo.Removable storage already attached to a VM – aborting.
GOTO END
:NOT_BOUND
echo.Storage device not bound to any VMs – aborting.
GOTO END
:END
endlocal
# ——————————————————————————————- #
Script usbmount.sh
#!/bin/bash
xe vbd-create vm-uuid=c145b8f0-7c3d-9208-c219-14cbec468911 device=autodetect vdi-uuid=146a5021-77a5-44b6-bcaa-edc5a1d4c822 > /marlo/vbduuid
vbduuid=$(cat /marlo/vbduuid)
xe vbd-plug uuid=$vbduuid
# ——————————————————————————————- #
Crédito : http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX118198
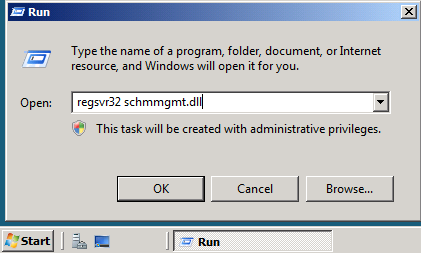


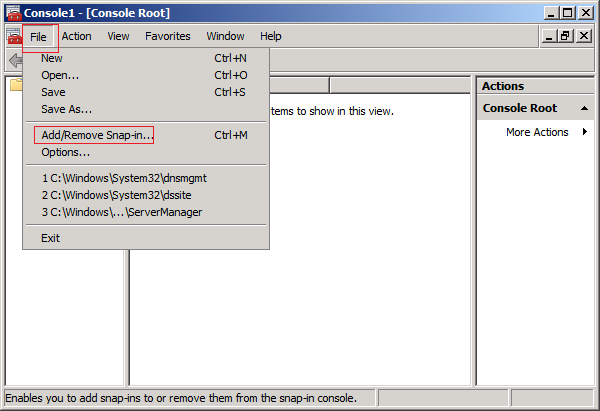
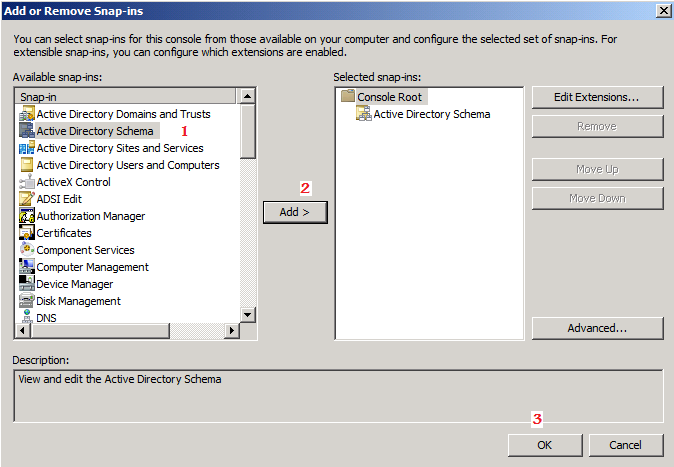

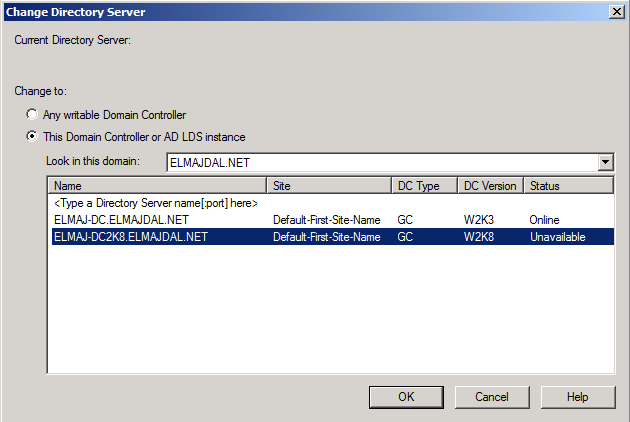
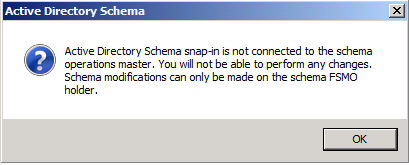
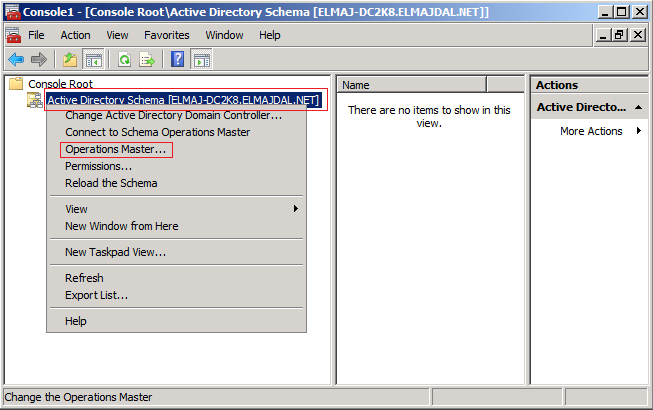
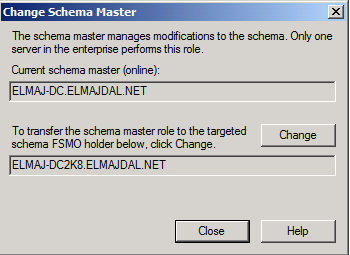 Click Yes to confirm the role transfer
Click Yes to confirm the role transfer